With countless online accounts and services to manage, the convenience of browser-based password managers can be tempting. Many browsers offer Autofill, which saves login credentials, making it easy to log in to websites quickly. However, convenience should not come at the expense of security. Storing passwords in a built-in password manager can pose significant risks to your Northeast Ohio business.
The Dangers of Browser-Based Password Managers
Here are some key reasons why you may want to rethink using browser password managers:
1. Limited Encryption:
Many browser-based password managers don’t use strong encryption methods. While they might encrypt your master password, your saved passwords could still be stored in plain text, making them easy targets for hackers.
2. Vulnerabilities in Browsers:
Web browsers are complicated pieces of software, and they come with their own set of security flaws. Cybercriminals often take advantage of these vulnerabilities, which can put your password manager data at risk—even with regular updates.
3. Lack of Security Features:
Some browser-based password managers lack crucial security measures, such as Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). This can leave your accounts more exposed and vulnerable to unauthorized access.
4. Shared Device Risks:
If you share your device with friends, family, or colleagues, they could easily access your browser-based password manager. Most don’t require any additional security checks, putting your valuable information at risk.
5. Malicious Extensions:
While browser extensions can add some great functionality, they can also bring security risks. Some extensions might be malicious or compromised, potentially allowing them to access your password manager data and jeopardize your stored passwords.
Removing Passwords Stored in Chrome, Firefox, and Safari
If you’ve been using browser password management and want to switch to a more secure solution, removing your stored passwords and personal information from your browser is a smart move. Here’s how you can do it:
Google Chrome:
Go to “Settings > Autofill > Passwords” and click on the three dots next to each saved password to remove them.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/001_show-passwords-in-chrome-4580283-9b9244527d8e4a73ae89edf737e295f3.jpg)
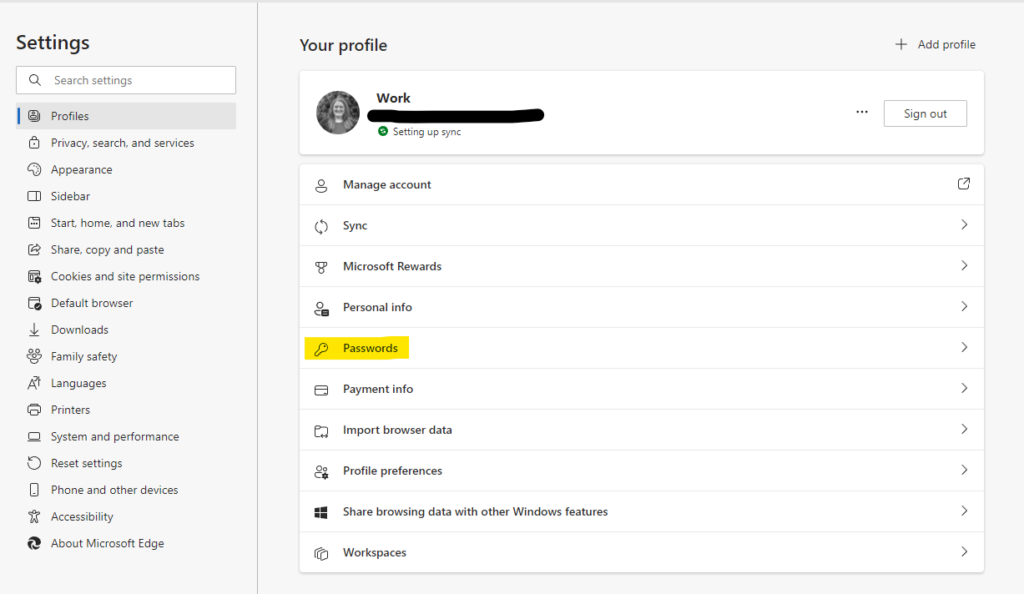
Microsoft edge:
Open your browser menu, go to “Settings,” then “Profiles,” and click “Passwords.”
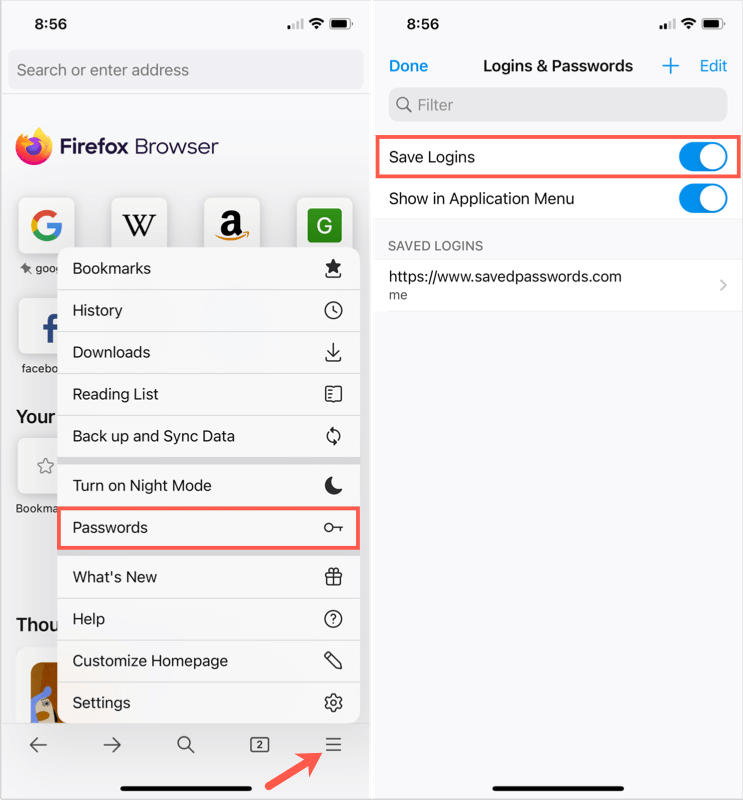
Firefox:
Open the Options menu, go to “Privacy & Security,” scroll down to “Logins and Passwords,” and click “Saved Logins.” From there, you can remove any stored passwords.
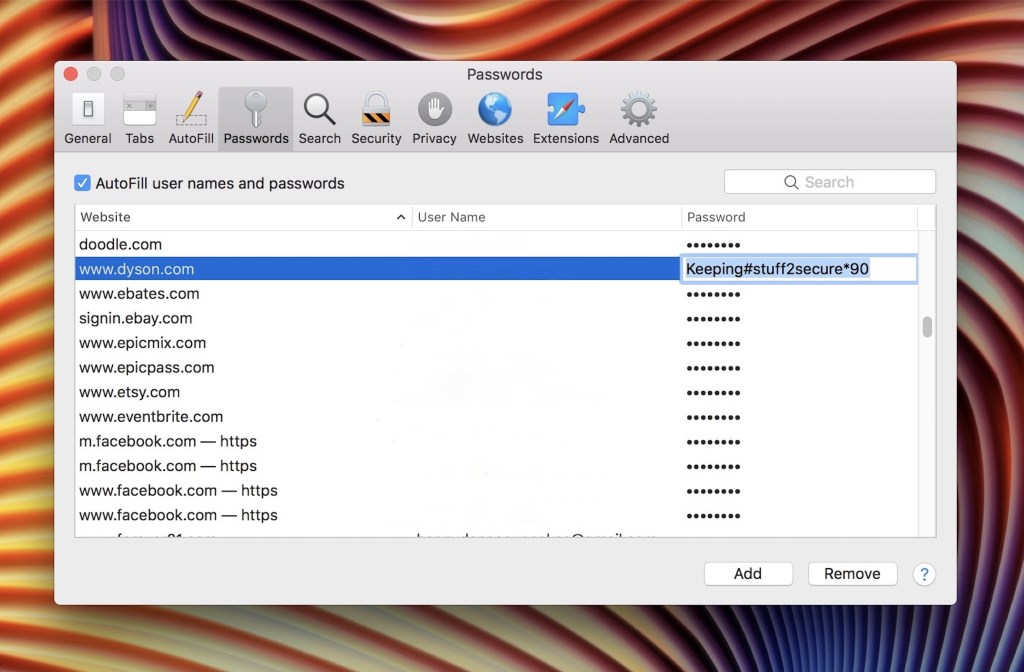
safari:
Open Safari “Preferences,” go to the “Passwords” tab, and select the passwords you want to remove. Click on the “Remove” button to delete them.
The Safer Alternative To Browser-Based Password Managers
Using dedicated password managers is a safer option since they provide enhanced security and various features to safeguard sensitive information. Here’s why:
1. Enhanced security:
Dedicated password managers use advanced encryption, making it difficult for cybercriminals to access sensitive information.
2. Cross-Platform Compatibility:
Dedicated password managers can be used across multiple devices and operating systems, ensuring consistent and secure access to your passwords.
3. Multi-factor authentication (mfa):
Many password managers offer MFA, requiring a secondary verification method for account access.
4. password strength analysis:
These managers often include tools that analyze the strength of your passwords, helping you create unique and strong passwords for each of your accounts.
5. secure password sharing:
Dedicated password managers enable the secure sharing of passwords with trusted individuals or team members without compromising the security of personal data.
Conclusion | Browser-Based Password Managers
In summary, while browser-based password managers may offer convenience, they come with significant risks. Opting for a dedicated password manager not only keeps your information secure but also enables you to enjoy peace of mind.
If you need more assistance with cybersecurity for your business, click here to reach out to the experts at AtNetPlus.
Sources:
